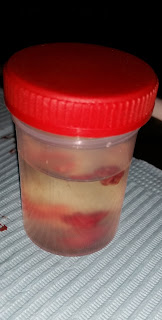
An 18-year-old female patients came to the OMFS department with complaint of discomfort on chewing. Oral examination revealed a pinkish-red colored lesion on buccal and lingual gingiva in the interdental area of mandibular central incisors. Lesion was soft in consistency and measured approximately 2 cm in diameter. Patient said that it's been there for two months.
Excisional biopsy was performed by the oral surgeon.
Considering the gingival location, the top entities in our differential diagnosis were pyogenic granuloma, peripheral ossifying fibroma and peripheral giant cell granuloma.
Microscopic examination showed a nodule of mucosa surfaced by stratified squamous epithelium. The body of nodule was composed of benign proliferation of plump fibroblasts. Bone formation is identified in some portions. Based on this histopathological presentation, a diagnosis of peripheral ossifying fibroma was made.
 |
| Histological slide showing plump fibroblasts and calcifications |
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma:
The peripheral ossifying fibroma is a benign
proliferation that occurs exclusively on the gingiva. It is seen more commonly
in teenagers and young adults. It usually presents as a pedunculate or sessile
nodular mass in the interdental region clinically. The color of the nodule
ranges from red to pink depending on the degree of irritation.
Conservative surgical
excision is the preferred form of management for this process. Despite their
benign nature, these lesions have the ability to become pretty large.